Products”TAMAKONA” &” MILKONA”
What are Tamakona and Milkona
Tamakona and Milkona are innovative products designed to streamline your oral food challenge tests and support patients and their families by simplifying daily intake at home.
Tamakona is a cooked whole egg powder, and Milkona is a skimmed cow’s milk powder. Both products are foods that are precisely quantified for protein denaturation and protein content.
How Tamakona and Milkona Can Help You
1. Simplifying Oral Food Challenge Tests in Medical Facilities:-
Tamakona revolutionizes the process of conducting food challenge tests in medical settings. With no need for complex measurements, Tamakona can be quickly and easily dissolved in a small amount of water, making the preparation of food challenge tests straightforward and efficient.
FAQ
- When using Tamakona or Milkona for oral food challenge tests, how many doses should be administered?
-
Please consider the severity of your patient’s condition, the anticipated allergic reactions, and the likelihood of these reactions occurring. Administer the doses according to your clinical judgment. It may also be beneficial to refer to guidelines from various countries for additional guidance.
2. Making Home Consumption Easy and Safe:-
For patients who need to continue consuming allergens at home after a negative oral food challenge test, Tamakona offers a convenient solution. Its precisely measured portions allow for accurate and easy consumption without the hassle of preparation, ensuring both safety and simplicity for patients and their families.
3. Facilitating Early Introduction of Allergenic Foods in Infants:-
Introducing allergens like eggs early in a child’s diet can significantly reduce the risk of developing allergies. Tamakona makes it easy to introduce small amounts of egg safely. Research indicates that starting with small amounts of egg at six months of age, alongside eczema treatment, can reduce the incidence of egg allergies by approximately 80% (Natsume et al. Lancet. 2017).
How to Use
Preparation is Simple and Quick!
The video below demonstrates how you can complete the preparation in just 20 seconds.
The product information
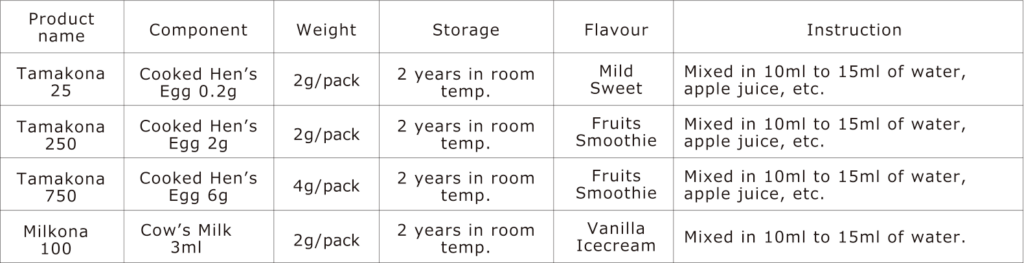
Tamakona 25
Tamakona 25 contains 25mg of egg protein (Kjeldahl method).
It is equivalent to approximately 0.2g of whole egg boiled for at least 15 minutes which includes 0.13g of boiled egg white.
Tamakona 250
Tamakona 250 meets the “low dose” of OFC according to the Japanese guideline for food allergy.
It contains 250 mg of egg protein (Kjeldahl method).
It is equivalent to approximately 2 g of whole egg boiled for at least 15 minutes which includes 1.3 g of boiled egg white. It is equal to 1/32-1/25 of a whole egg.
Tamakona 750
Tamakona 750 meets the “medium dose” of OFC according to the Japanese guideline for food allergy.
It contains 750 mg of egg protein (Kjeldahl method).
It is equivalent to approximately 6 g of whole egg boiled for at least 15 minutes which includes 4 g of boiled egg white.
It is equal to 1/8 of a whole egg.
Milkona 100
Milkona 100 meets the “low dose” of OFC according to the Japanese guideline for food allergy.
It contains 100mg of milk protein (Kjeldahl method), which is equivalent to 3ml of milk.
Because it is made from skimmed milk powder, its antigenicity may be slightly lower than that of 3ml of raw cow’s milk.
Table. Product information
Evidences of Tamakona and Milkona powder
【Oral food challenge】
Egg
- Stepwise single-dose oral egg challenge: a multicenter prospective study. Yanagida et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2019; 7: 716-8.e6.
(Further information is provided below) - Timing of onset of allergic symptoms following low-dose milk and egg challenges. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2021; 32: 612-5
(Further information is provided below) - Threshold and safe ingestion dose among infants sensitized to hen’s egg. Mitomori et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2022; 33: e13830.
(Further information is provided below)
Milk
- Increasing specific immunoglobulin E levels correlate with the risk of anaphylaxis during an oral food challenge. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2018; 29: 417-24
- Relationship between serum allergen-specific immunoglobulin E and threshold dose in an oral food challenge. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2023; 34: e13926.
【Daily intake at home and oral immunotherapy】
Egg
- Safe egg yolk consumption after a negative result for low-dose egg oral food challenge. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2021; 32: 170-6
(refer to the information below for further details) - Long-term outcomes of oral immunotherapy for anaphylactic egg allergy in children. Sasamoto et al. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: Global 2022;1: 138-144.
Milk
- Safe consumption of processed foods after negative medium-dose cow’s milk oral food challenge. Vanlaya et al. Allergology Int 2023 (in press)
- A randomized trial of oral immunotherapy for pediatric cow’s milk-induced anaphylaxis: Heated vs unheated milk. Nagakura et al. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2021; 32: 161-9
(Further information is provided below)
【Baby food and prevention】
Egg
- Two-step egg introduction for prevention of egg allergy in high-risk infants with eczema (PETIT): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Natsume et al. Lancet 2017; 389: 276-286
(Further information is provided below)
Evidence 1 : Stepwise single-dose oral egg challenge: a multicenter prospective study. Yanagida et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2019; 7: 716-8.e6
We conducted stepwise oral food challenges (OFC) using the same powder as Tamakona 250 and Tamakona 750 at 4 hospitals and 3 clinics in Japan. The study included 252 patients with a history of egg allergy, whose median age was 1.7 years (interquartile range (IQR) of 1.2-4.6 years). The median total IgE was 172 IU/mL (IQR: 53-611), egg white specific IgE was 14.3 kUA/L (IQR: 4.3-33.8), and obomucoid specific IgE was 7.5 kUA/L (IQR: 1.6-24.5).
Out of the 252 patients who underwent OFC with Tamakona 250, 200 (79.3%) were asymptomatic and had a negative result of OFC. The remaining 52 patients tested positive, out of which 13 (25%) had mild symptoms, 38 (73%) had moderate symptoms, and 1 (2%) had severe symptoms. The onset of symptoms was recorded after 61 minutes (ranging from 25 to 102minutes) from loading, peaked at 80 minutes (20 to 138), and resolved at 120 minutes (84 to 180). Oral antihistamines were given to 34 patients (65%), oral steroids to 15 patients (29%), and inhaled beta2-stimulants to 5 patients (10%). No severe cases required intramuscular adrenaline injection (0%).
Similarly, out of 154 patients who underwent OFC with Tamakona 750, 148 (96%) were asymptomatic and had a negative result of OFC. Of the 16 positive cases, 4 (25%) experienced mild symptoms and 12 (75%) had moderate symptoms, but no case (0%) had severe symptoms. The onset of symptoms was recorded after 48 minutes (28-90) from loading, peaked at 65 minutes (49-100), and resolved at 133 minutes (86-153). Oral antihistamines were administered to 13 patients (81%), oral steroids to 6 patients (38%), and beta2-stimulant inhalation to 4 patients (25%). No severe cases required intramuscular adrenaline injection.
Evidence 2 : Timing of onset of allergic symptoms following low-dose milk and egg challenges. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2021; 32: 612-5
We conducted an observational study of OFC with Tamakona 250 and Milkona 100 on children with a history of reaction or sensitization proven by elevated IgE level. Out of 563 children, 53 (9.4%) passed the OFC using Tamakona 250, while 20 out of 103 (19%) passed the OFC using Milkona 100. The symptoms appeared after 60 minutes (median) and 30 minutes (median) after loading Tamakona 250 and Milkona 100, respectively. In conclusion, during OFC, allergic reactions to milk appear and resolve sooner than reactions to hen’s egg, regardless of the total amount of food protein ingested and its form (unbaked vs. baked in a grain matrix). Our findings can help improve the safety of OFCs. We also confirmed that the test can be safely administered to children with or suspected of having hen’s egg or cow’s milk allergy.
Evidence 3 : Threshold and safe ingestion dose among infants sensitized to hen’s egg. Mitomori et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2022; 33: e13830
The study analyzed the outcome of a stepwise OFC in infants who had not eaten hen’s eggs but who were sensitized to egg white-specific IgE. The enrolled infants had a median age of 9.9 months, with a total IgE level of 101 IU/mL, egg white-specific IgE level of 18.0 kUA/L, and obomucoid-specific IgE level of 0.99 kUA/L. A low dose OFC as part of the stepwise OFC was performed using with Tamakona 250. Out of the 87 patients, 12 (14%) failed the low dose OFC, and one patient (1.1%) required an adrenaline intramuscular injection. Subsequently, a moderate dose OFC with Tamakona 750 was performed on 75 patients, and 9 (12%) failed. The study showed that a stepwise OFC performed on infants who were not fed and had IgE sensitization was relatively safe, with many children avoiding complete elimination.
Evidence 4 : Safe egg yolk consumption after a negative result for low-dose egg oral food challenge. Yanagida et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2021; 32: 170-6
A clinical study was conducted with 276 subjects, who had a median age of 1.2 years, a total IgE of 104 IU/mL, egg white-specific IgE of 14.7 kUA/L, and obomucoid-specific IgE 5.3 kUA/L. he subjects were instructed to consume egg yolk splice at home after a low dose OFC with Tamakona 250 was negative. Out of the 276 subjects, only 6 (2.1%) experienced minor symptoms at home. Among these, 5 were able to continue consuming the egg yolk binder without any issues, while 1 patient experienced mild respiratory symptoms, resulting in the complete elimination of the egg yolk binder. Based on the above findings, it is considered that egg yolk bridges can be safely consumed if the Tamakona 250 OFC is negative.
Evidence 5 : Two-step egg introduction for prevention of egg allergy in high-risk infants with eczema (PETIT): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Natsume et al. Lancet 2017; 389: 276-286
This study included infants who had itchy eczema or atopic dermatitis within a few months of birth. Their eczema was cured by appropriate skincare and use of topical steroids by the time they turned 6 months old. From 6 months of age, a very small amount of cooked whole egg powder, equivalent to Tamakona 25, was given once a day to the infants. At 9 months of age, the amount was increased to about 5 times, equivalent to half of Tamakona 250. The safety of the procedure was confirmed by OFC at the beginning of the study and when increasing the amount of food. An equal number of infants were also given the placebo powder which did not include hen’s eggs for comparison. When the infants were 1 year old, the number of children who showed allergic reactions to the equivalent of about half a cooked whole egg was compared between the two groups. The group that ate cooked whole egg powder had a lower prevalence of children who showed allergic reactions compared with the group that ate placebo powder.
This study was published in 2017, and in response, the Japanese Society of Pediatric Allergy issued a “Recommendation on the Prevention of the Development of Egg Allergy” and recommended that the consumption of eggs in weaning food should not be delayed in order to prevent the onset of egg allergy. 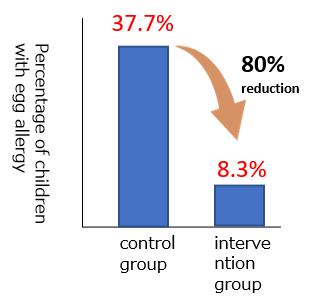
Modified from Natsume O, Kabashima S, et.al.Lancet. 2017 Jan 21;389(10066):276-286
Note
These products can be used in OFC as well as other egg- and milk-containing foods. Allergic symptoms may be induced if they are ingested by a person suffering from an allergy. OFC is a medical procedure conducted by physician experts at a medical institution under the clinical guidelines and should not be conducted by parents or guardians at home. If parents or guardians have any concerns about food allergies, please consult your home doctor or a specialist nearby.

